lv function heart | what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle lv function heart The left ventricle is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Left ventricular contraction forces oxygenated blood through the aortic valve to be distributed to the entire body. With such an important role, decreased function caused by injury or maladaptive change can induce disease symptoms. Indulge in unique experiences and the ultimate escape at Excalibur Hotel & Casino, MGM Collection, now participating in Marriott Bonvoy. Discover new ways to earn and redeem points in Las Vegas and beyond.
0 · why is left ventricle thicker
1 · what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle
2 · picture of left ventricle heart
3 · left ventricular hypertrophy life expectancy
4 · left ventricle receives blood from
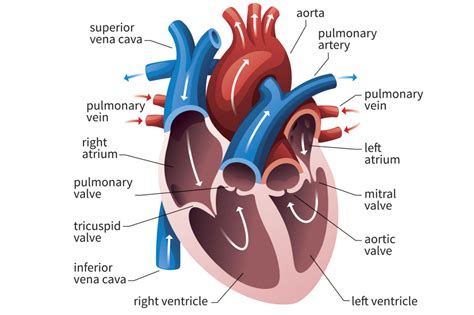
5 · left ventricle heart diagram
6 · left ventricle function and location
7 · Lv ejection fraction chart
Paldies par reģistrēšanos "EUROBIKE" lapā! Jums tiks paziņots uz e-pastu, tiklīdz jūsu profils būs aktivizēts. Ja jums ir JEBKĀDI jautājumi par šīs vietnes darbību līdzu sazinieties ar mums.
why is left ventricle thicker
The left ventricle is the chamber of the heart that pumps oxygenated blood to the body. Learn about its structure, location, valves and common conditions that affect its function. The left ventricle is the thickest of the heart’s chambers and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to tissues all over the body. By contrast, the right ventricle solely pumps blood to. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure.
An accurate left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) reading can be measured through a variety of imaging techniques. The most common ejection fraction testing measures include: Echocardiogram. An.
The left ventricle is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Left ventricular contraction forces oxygenated blood through the aortic valve to be distributed to the entire body. With such an important role, decreased function caused by injury or maladaptive change can induce disease symptoms.
Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood. Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each contraction. LVEF helps determine the severity of dysfunction on the left side of the heart. According to the American Heart Association: A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Even if you have a normal ejection fraction, your overall heart function may not be healthy.
Assessment of the size, mass, geometry, and function of the left ventricle is fundamental for the diagnosis and prognosis of most cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, structural heart disease, etc.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the volume of blood pumped out of the heart during systole relative to the volume in the left ventricle at the end of diastole. LVEF is calculated using the following equation: LVEF = SV / EDV. Organ Connection. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).
The left ventricle is the thickest of the heart’s chambers and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to tissues all over the body. By contrast, the right ventricle solely pumps blood to. A normal heart’s ejection fraction is between 55 and 70 percent. This indication of how well your heart is pumping out blood can help to diagnose and track heart failure. It is important to note, however, that you can have a normal ejection fraction measurement and still have heart failure. An accurate left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) reading can be measured through a variety of imaging techniques. The most common ejection fraction testing measures include: Echocardiogram. An. The left ventricle is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Left ventricular contraction forces oxygenated blood through the aortic valve to be distributed to the entire body. With such an important role, decreased function caused by injury or maladaptive change can induce disease symptoms.
Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood. Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each contraction. LVEF helps determine the severity of dysfunction on the left side of the heart.
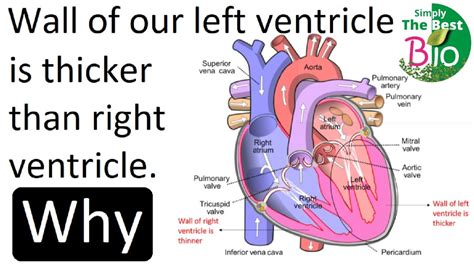
what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle
According to the American Heart Association: A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Even if you have a normal ejection fraction, your overall heart function may not be healthy.Assessment of the size, mass, geometry, and function of the left ventricle is fundamental for the diagnosis and prognosis of most cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, structural heart disease, etc.Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the volume of blood pumped out of the heart during systole relative to the volume in the left ventricle at the end of diastole. LVEF is calculated using the following equation: LVEF = SV / EDV. Organ Connection.
Overview. Eternatus is the premier dedicated Kyogre check in Ubers, able to tank even boosted Ice Beams and stall Kyogre out with Toxic and Recover. Additionally, its access to, and ability to absorb, Toxic Spikes give it great utility in .Saimniecības ēku būvniecība. Vairāk nekā 100 gadu pieredze un nepārtraukta sadarbība ar lauksaimniecības nozari ir ļāvusi mums radīt jumta risinājumus, kas atbilst Eiropas lauksaimnieku vajadzībām. Eternit viļņotās loksnes un aksesuāri ir .
lv function heart|what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle